Introduction on FS 42U GR Series Network & Server Cabinets
Network & server cabinets are integral to the success of a good data center construction. Because they could provide platforms for housing networking devices such as servers, rack mount enclosures. In this way, the devices are kept on racks and cables can be easily bundled, which is good for maintaining the devices and ensuring network performance. To meet customers’ demands like cooling, device and cable management, network equipment security and ease of installation, FS has released 42U GR600 and GR800 network & server cabinet. GR600 is a server cabinet, while GR800 can be used as network and server cabinet, what’s the difference between them? Here introduces GR series network & server cabinets’ highlights first, then explains their different applications and advantages.
FS 42U GR series Network & Server Cabinets Highlights
FS 42U rack cabinets can accommodate all 19 inches EIA standard networking equipment. These server racks use SPCC cold roll steel material, which is firm and durable. They consist of some major components, removable front and rear doors, four lockable and removable side panels and four adjustable vertical mounting rails.
- Doors: Both the front and rear doors use the perforation design, allowing the massive front to rear airflow up to 78%, which has exceeded IT equipment airflow requirement (63%). Besides, the rear doors are split which makes access easier.
- Side panels: The side panels are half size (two per side) for ease of removal and reinstallation. They have no vents which can prevent hot air from recirculating through the sides of the rack and maintain direct front to rear airflow. Thus, they can improve cooling efficiency. These side doors can be locked and removed easily for simple handling and access to the equipment.
- Vertical mounting rails: The vertical rails can be adjusted to accommodate any mounting requirement for IT equipment. Besides, the rails feature squarer holes for cabling, which makes it easier to route cabling to the installed rack equipment.
FS also provide a complete range of accessories to meet different requirements, including two full height dual PDU brackets, two adjustable fixed shelves and so on.
GR600 vs GR800 Network & Server Cabinet, What’ s the Difference?
Both the two network & server cabinets are the solutions for protecting and organizing the network infrastructure in data centers. The following aspects are the main differences between the two cabinets.
As the names imply, the two rack cabinets have different widths. GR600 type uses 2038x600x1170mm design, while the dimension of GR800 is 2038x800x1170mm. If you are using server cabinet for connecting switches and other networking devices with much cabling complexity, then GR800 is recommended as this will offer a lot more space for cable management.
The top panel of GR600 is equipped with one-sided brush strip for resisting flame, and its vertical mounting rails have no cable access ports. And it has two adjustable fixed shelves for supporting equipment without rack-mounted brackets like UPS units. On the other hand, GR800 top panel adopts tow-sided brush strips design. And there’re plastic cables outlets on the rails for routing. Plus, it’s equipped with two vertical cable managers for managing cables.
Due to different designs and accessories, they are used in different applications for housing different devices. GR600 is usually used as the server cabinet for installing servers, monitors or similar equipment. While GR800 can also be used as the server cabinet, simultaneously, it can serve as the network cabinet for accommodating routers, network switches and cable management accessories like fiber enclosure, adapter panel and cassette. Note that, it’s better to use them in the right way. Because improperly housing the heat-producing equipment is dangerous, which may cause damage to the equipment or even a fire.
Which to Choose?
From the above, we know FS GR600 and GR800 rack cabinets are ideal for high density data center environments, providing excellent accessibility and thermal efficiency. But for some different designs and accessories, they have different usages. If you just need to house servers, monitors and UPSs, and has a small budget, GR600 server cabinet is a good choice for you. But for GR800, it’s more suitable for the users who have higher density and more complex cabling demands. Because GR800 not only can house the servers, patch panels, but also can handle a mass of cables used to connect the switches and other devices.
FS GR series 42U network & server cabinet, available on the same day shipping with flat package, is the cost-effective rack cabinet. Plus, before and after your purchase, our technical support are available to assist you by phone (+1 (888) 468 7419) and live chat.
Is MLAG an Alternative to Stackable Switches?
With the demands for resiliency and security for today’s networks, modern enterprises and data center networks are becoming more complex to manage and operate. MLAG and stacking both are the scalable solutions that can reduce network complexity and improve network performance. Are they the same? Can users consider MLAG as an alternative to stacking switches? This article explains this through introducing MLAG and stackable switches, and the difference.
MLAG Explained
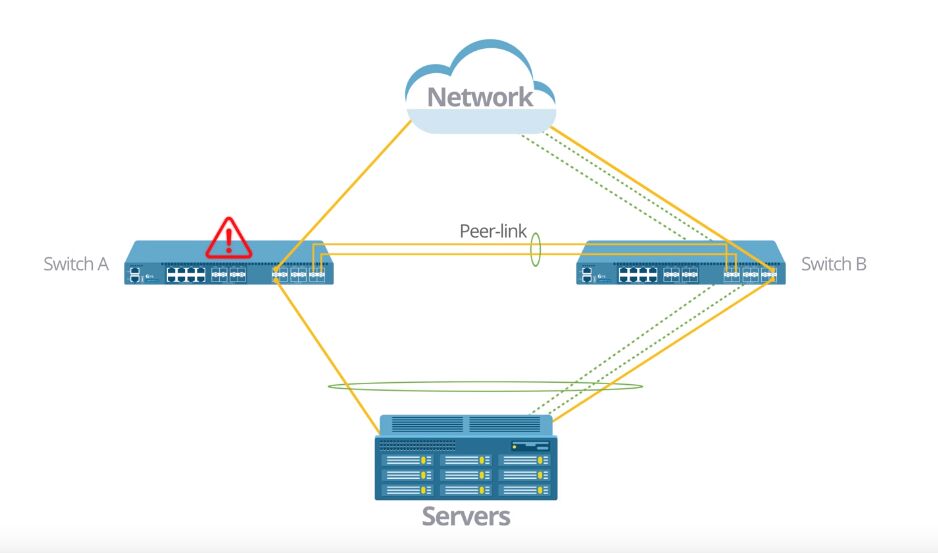
MLAG refers to multi-chassis link aggregation group, which is a technique used on network switches to enable the fast and inexpensive transmission of bulk data. It enables a server or network switch with a two-port bond, such as LAG, EtherChannel, port group or trunk, to connect those ports to different switches and operate as if they are connected to a single, logical network switch. MLAG can provide redundancy and system throughput. The following is an MLAG example. If switch A breaks down, the servers can still access the network because all the data will be transferred through switch B by MLAG. MLAG implements a backup link aggregation group between switch A and
Figure 1: MLAG example.
Stackable Switch Explained
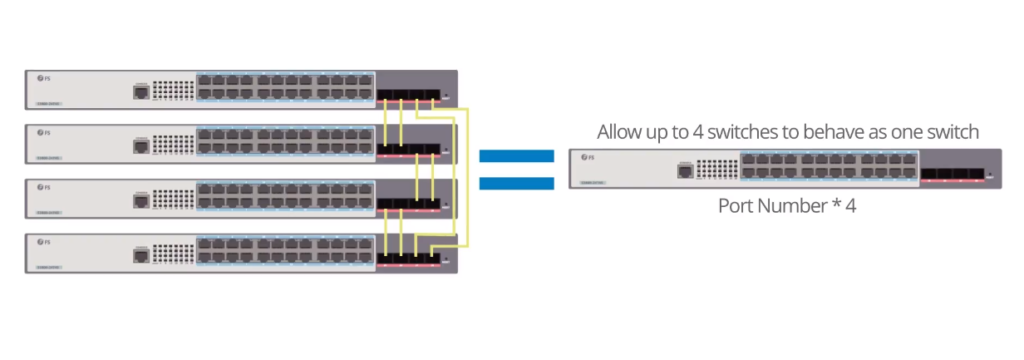
Stackable switches are a type of network switches that are designed to be stacked on top of one another by connecting the
Figure 2: Four 24 port switches can be stacked together.
What’s the Difference?
Both MLAG and switch stacking allow multiple switches to act as one by sharing information. But they are different technologies with their own pros and cons.
MLAG provides higher bandwidth links as network traffic increases. And the traffic is more evenly distributed to each switch by using LAG hashing. Each switch is independently able for forwarding traffic without passing to a master switch. MLAG can expand port capacity beyond the limitation of switch stacking. However, MLAG configuration is more complex that users have to configure each switch individually.
On the other hand, the configuration of switch stacking is simpler since all the configurations can be done in the master switch. The ports density can be increased by adding another Gigabit Ethernet switch to the stack. This is more suitable for small sites. And it makes sense to be used at the edge where the control plane services are not required for the full functioning of the network. However, the number of switches that can be stacked is limited. This maximum number can be 6,8,12,16, etc. Stacking in networking creates more inter-switch communications when compared to the ISC for MLAG. Besides, switch stacking can only increase the port density but not the bandwidth.
Which to Choose?
MLAG and switch stacking can improve the performance of data
To meet different networking demands, FS offers both MLAG and stacking solution. The S5800, S5850, S8050, N5850 series switches support MLAG, ranging from 10G to 100G transmission speed. With the support of MLAG, these network switches provide redundancy protection for your networks. FS S3900 series switches are stackable switches with 24 or 48 ports, including both fiber and
Web-scale vs Hyperconverged Infrastructure: What Is the Difference?
As virtualization
What Is Web-scale Infrastructure?
Web-scale architecture describes computing environments that allow applications to be decomposed into web services. Essentially, a web-scale network acts as a single unit which can grow and change based on network demands, without the need to manually reconfigure multiple network switches. Note that, the primary way web-scale networks achieve this flexibility and automation is through decoupling the hardware (physical network switch) and software (network operating system). Thus, customers are no longer locked into one vendor’s hardware. They are free to choose the bare metal hardware (like a Gigabit Ethernet switch) and software by
What Is Hyperconverged Infrastructure?
Web-scale vs Hyperconverged Infrastructure: What Is the Difference?
The following are the major architectural factors that differentiate web-scale from
Web-scale deployments rely on software abstractions. This is mainly because hardware abstractions impose strict consistency requirements, which are extremely difficult to scale. Meanwhile, software abstractions can be tuned for a specific workload, providing reduced consistency and scale while preserving performance and availability. And web-scale companies sometimes combine compute and storage for given services, but usually divide applications into different services. Therefore, in many cases, different services may have completely separate hardware to suit a specific application. For instance, Facebook and Google have all publicly declared that they use different hardware for the appropriate service.
Hyperconverged system
Web-scale infrastructure relies on custom hardware. Web-scale companies prefer to use custom devices since they can suit the specific applications requirements or the reduced overall cost. For example, Amazon has stated that it uses custom hardware configurations and switches to fit its data center requirements.
On the other hand,
In addition,
Which One to Choose?
From the above, we know web-scale infrastructure heavily relies on hardware customization. It uses software abstractions provided by applications for scale. Hardware and applications are heavily coupled and customized for
So which one
SFP Fiber Switch Introduction and Cabling Solutions
With the growth of today’s network, the amount of hardware involved has become a barrier to efficient and optimized network operations. In some cases, a fiber switch is
SFP Fiber Switch Introduction
As the name implies, an SFP fiber switch is a communication control device with SFP ports. And like a common networking switch, SFP fiber switch is also used to send and receive
Advantages of SFP Fiber Switch
SFP fiber switch can provide a higher reliability and security than the RJ45 port switch. As we know, fiber cables transfer data in light, which is faster than the copper cables’ electronic transmission speed. And due to the special design of fibers, the SFP fiber switch generates less data loss and electromagnetic interference. Therefore, using an SFP fiber switch is better than the RJ45 port copper switch. For example, if the transmitting distance is more than 100 meters, copper cables like Cat5e or Cat6a is unable to reach. So you need the fiber cables which are often used to interconnect switches in multi-building deployments.
FS SFP Fiber Switch Cabling Solution
To meet the market demands, FS.COM has published a set of fiber switches and the corresponding cabling solutions. Here we take S5800-48F4S SFP fiber switch as an example. Before we learn its cabling solutions, let’s have a look at the fiber switch first.
This SFP network switch is a 10GbE switch. It’ s designed with 48 1GbE SFP ports and 4 10GbE SFP+ ports, which allows
As the video shows, a completed cabling solution of a fiber switch includes transceiver and fiber cables. Here S5800-48F4S switch can support 1G SFP, 1GBASE-T and 10G SFP+ transceivers. So we list some supported transceivers as shown in table 1 for your reference.
|
Transceiver ID
|
Description
|
Price (US dollars)
|
|
20057
|
1000BASE-T SFP Copper RJ-45 100m Transceiver Module
|
$21
|
|
29838
|
1000BASE-SX SFP 850nm 550m DOM Transceiver Module
|
$6
|
|
29853
|
1000BASE-EX SFP 1310nm 40km DOM Transceiver Module
|
$14
|
|
29854
|
1000BASE-EX SFP 1550nm 40km DOM Transceiver Module
|
$24
|
|
29856
|
1000BASE-ZX SFP 1550nm 80km DOM Transceiver Module
|
$24
|
|
11589
|
10GBASE-SR SFP+ 850nm 300m DOM Transceiver Module
|
$16
|
|
11591
|
10GBASE-LR SFP+ 1310nm 10km DOM Transceiver Module
|
$34
|
Table 1
The following table 2 are the supported cables that can be used for connecting S5800-48F4S switch to other networking equipment.
|
Fiber ID
|
Fiber Connector
|
Fiber Mode
|
1M Price (US dollars)
|
|
70603
|
Unshielded
|
Cat6
|
$1.7
|
|
70733
|
Unshielded
|
Cat6
|
$1.7
|
|
68477
|
LC UPC to LC UPC
|
OM4 50/125μm
|
$6.6
|
|
68299
|
LC UPC to LC UPC
|
OM4 50/125μm
|
$4.5
|
|
62397
|
LC-LC
|
OS2 SMF
|
$11
|
|
68294
|
LC-LC
|
SMF 9/125μm
|
$8.4
|
Table 2
Conclusion
SFP fiber switch can actually improve overall speeds and responsiveness of one’s network. FS carries a full line of Gigabit Ethernet switch, including 8 port SFP fiber switch, 24 or 48 port fiber switch. Contact us via sales@fs.com for a free consultation on your networking needs and choose the suitable fiber switch based on your specific requirement.
GLC-SX-MM VS GLC-SX-MMD VS GLC-SX-MM-RGD VS SFP-GE-S
Cisco is a worldwide leader in the telecommunication industry whose routers, switches are very welcome among the users. To work well with those Cisco networking applications, Cisco SFP transceivers are the best choice. GLC-SX-MM, GLC-SX-MMD, GLC-SX-MM-RGD
Which transceiver module will you choose?
Cisco Transceiver Datasheet
Here are the datasheets of these four different Cisco SFP transceiver modules.
The GLC-SX-MM is programmed to be fully compatible and functional with all intended Cisco 1GB switching devices. This transceiver module operates on ordinary multimode fiber optic link spans of up to 550 meters in length.
|
Transceiver Module
|
GLC-SX-MM
|
|
Interface
|
LC duplex
|
|
Wavelength
|
850nm
|
|
Tx Power
|
-9.5 ~ - 3dBm
|
|
Receiver Sensitivity
|
< -17dBm
|
|
DOM Support
|
No
|
|
Temperature Range
|
0 to 70°C (32 to 158°F)
|
|
Cable Type
|
MMF
|
|
Price(US dollars)
|
6.00
|
The GLC-SX-MMD 1000BASE transceiver module is made for multimode fiber only. It’s the replacement of GLC-SX-MM which features an enhanced DOM interface. And this SFP fiber transceiver module operates on legacy 50 µm multimode fiber links up to 550 meters.
|
Transceiver Module
|
GLC-SX-MMD
|
|
Interface
|
LC duplex
|
|
Wavelength
|
850nm
|
|
Tx Power
|
-9.5 ~ - 3dBm
|
|
Receiver Sensitivity
|
< -17dBm
|
|
DOM Support
|
Yes
|
|
Temperature Range
|
0 to 70°C (32 to 158°F)
|
|
Cable Type
|
MMF
|
|
Price(US dollars)
|
6.00
|
The GLC-SX-MM-RGD transceiver module is designed for Industrial Ethernet applications, including factory automation, intelligent transportation system and other deployments in
|
Transceiver Module
|
GLC-SX-MM-RGD
|
|
Interface
|
LC duplex
|
|
Wavelength
|
850nm
|
|
Tx Power
|
-9.5 ~ - 3dBm
|
|
Receiver Sensitivity
|
< -17dBm
|
|
DOM Support
|
Yes
|
|
Temperature Range
|
-40 to 85°C (-40 to 185°F)
|
|
Cable Type
|
MMF
|
|
Price(US dollars)
|
6.00
|
The Cisco SFP-GE-S transceiver provides a high performance and cost-effective small form factor pluggable module for 1000BASE-SX Gigabit Ethernet and 1G Fiber Channel application. It’s designed for short wavelength applications. The max distance for this transceiver module is 550 meters. Besides, it also supports DOM.
|
Transceiver Module
|
SFP-GE-S
|
|
Interface
|
LC duplex
|
|
Wavelength
|
850nm
|
|
Tx Power
|
-9.5 ~ - 3dBm
|
|
Receiver Sensitivity
|
< -17dBm
|
|
DOM Support
|
Yes
|
|
Temperature Range
|
0 to 70°C (32 to 158°F)
|
|
Cable Type
|
MMF
|
|
Price(US dollars)
|
6.00
|
Differences of GLC-SX-MM VS GLC-SX-MMD VS GLC-SX-MM-RGD VS SFP-GE-S
From the above Cisco transceiver datasheet, we have learned that these Cisco transceiver modules share many similarities. All of them can support up to 550 meters over multimode fibers. And they are designed with the same 850m wavelength, Tx power
GLC-SX-MM, GLC-SX-MMD
Conclusion
According to the above discussion, we can say GLC-SX-MM, GLC-SX-MMD, GLC-SX-MM-RGD and SFP-GE-S transceivers share many similarities. However, please note that the differences still exist, and ensure the transceiver module you choose will be compatible with the existing networking equipment. FS.COM is the one-stop shop to help you get these Cisco transceivers and other networking products that are compatible with the Cisco transceivers. If you have any questions
Things About Cisco SFP Compatibility Matrix That Wiki Can’t Tell You
Overview of Cisco Copper SFP Transceiver Module
SFP stands for small form factor pluggable. Copper SFP transceiver is a hot-pluggable transceiver with RJ45 port, so it’s also called SFP RJ45 transceiver. SFP RJ45 transceiver supports 10/100/1000 BASE rate over Cat5 cables. In addition,
How to Choose A Cisco Copper SFP Transceiver Module
When you decide to buy a copper SFP transceiver, the quality and price matter a lot. But the price between OEM and the third party suppliers varies greatly. If you have plenty of money, you can order one directly from Cisco. If you search for a cost-effective solution, then the third party is a good choice. As for the quality, there are not many differences between Cisco and the third party’s products, because all products must meet the strict standards or MSA (Multisource Agreement). So it’s a wise decision to buy a copper SFP transceiver from a third party. Here I recommend you some copper SFP transceivers from FS.COM, whose transceivers are all tested before shipping.
Figure: Choose a suitable copper SFP transceiver for your network
This GLC-T transceiver is a typical RJ45 transceiver, which is used for Cat5 wiring. The max data rate is 1000Mbps and the max cable distance is 100 meters, which is suitable to connect different switches or routers in a data center. It’s compatible with most Cisco switches and some FS switches like S5800-48F4S Gigabit SFP switch.
Similar with GLC-T SFP, but this copper transceiver supports 10/100/1000 auto negotiation. And the operating temperature is different. It is an extended temperature range from -5 to 85°C, while GLC-T is from 0 to 70°C. Furthermore, it also operates on standard Cat5 unshielded twisted-pair copper cabling of link lengths up to 100 meters.
Cisco SFP Compatibility Matrix for GLC-T and GLC-TA
Both GLC-T and GLC-TA are supported on a wide range of Cisco equipment. Here
|
Switches Support GLC-T and GLC-TA
|
|
|
Cisco ME-2400-24TS-A
|
Cisco WS-C2940-8TF-S
|
|
Cisco ME-3400G-12CS-A
|
Cisco WS-C2960-24PC-L
|
|
Cisco ME-3400G-2CS-A
|
Cisco WS-C2960-48PST-L
|
|
Cisco ME-3400-24FS-A
|
Cisco WS-C2960G-48TC-L
|
|
Cisco 3750 ME-C3750-24TE-M
|
Cisco WS-C2960S-24TS-S
|
|
Cisco ME-3600X-24FS-M (SFP ports)
|
Cisco 2960S-F48TS-S
|
|
Cisco ME-3800X-24FS-M (client ports)
|
Cisco WS-C2970G-24TS-E
|
|
Cisco 4900 ME-4924-10GE
|
Cisco WS-C2975GS-48PS-L
|
|
Cisco 6500 ME-C6524GS-8S
|
Cisco WS-C3560-24PS
|
|
Cisco 2900 WS-C2948G-GE-TX
|
Cisco WS-C3560G-48TS
|
|
More supportable switches, please check Cisco Transceiver Compatibility Matrix.
|
|
Besides Cisco switches, GLC-T and GLC-TA can also be used on FS.COM S5800-48F4S switch which is a 48 port SFP L2/L3 MPLS switch with 4 10G SFP+ ports. It is a very cost-effective solution for
Conclusion
Knowing Cisco SFP compatibility matrix can help us to choose the suitable transceiver and switch quickly. Cisco copper SFP transceiver modules produced by FS.COM can work well with Cisco switches and FS switches. Besides, our Cisco compatible SFPs are the most reliable quality products without
Will Cat6 Patch Panel Work with Cat6a Cable?
As information technology develops, we have to upgrade our network products such as the cables, patch panels, etc. Besides, to reduce our data center’s cost, we are tempted to use the old and new ones to make a mixed connection. For instance, run Cat6a cables on
Comparison of Cat6 and Cat6a Cabling
Cat6a and Cat6 are both designed for Gigabit Ethernet. They can handle 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-TX, and 10GBASE-T rate. Cat6 and Cat6a sound almost the same, but a single lowercase “a” sets the two terms apart. The word “a” stands for augmented, which makes them behave differently in performance, size and so on.
Cat6 usually has 23 AWG wire
Can I Use Cat6a Cables on Cat6 Patch Panel?
Ethernet patch panel is the easiest method currently for your networking needs by providing a reliable and neat Cat6 and Cat6a cabling. Usually, we use
Cat6a is the updated version of Cat6, they share the same RJ45 connectors. Therefore, it’s no doubt that Cat6a cables can be plugged into the Cat6 patch panel.
Cat6a cable’s size is bigger, so the corresponding minimum bend radius is larger, which will change installation requirements for routing and handling as well as
Commonly, conductors determine whether the connection works or not. Thus, in this respect, Cat6 patch panel will work with Cat6a cables, since they have the same RJ45 conductors. But from the
Conclusion
To sum up, Cat6a cables are able to run on
Related Article: Does Cat6 on Cat5e Patch Panel or Cat5e on Cat6 Patch Panel Work?